☰

Mach 9.59 HB2 configuration
Axially-symmetric flow-field | Cold hypersonics
![]() Working directory located here
Working directory located here
![]() J.-J. O.E. Hoste and V. Casseau, "Verification and Validation of hyFoam for Supersonic External Flows," TechReport-HS1, 05/2021 [PDF→]
J.-J. O.E. Hoste and V. Casseau, "Verification and Validation of hyFoam for Supersonic External Flows," TechReport-HS1, 05/2021 [PDF→]
1. CASE SETUP
1.1 Geometry & Mesh
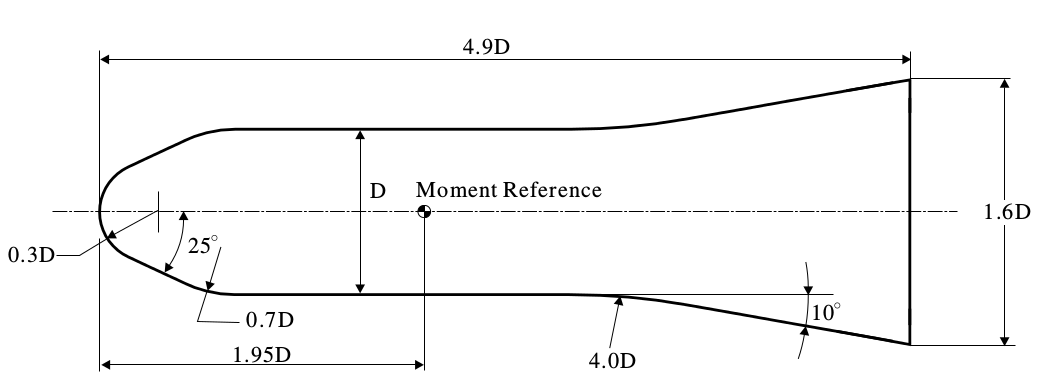
Geometry of the HB-2 flare (D is equal 0.1 m)
Views of the 2-D axisymmetric mesh (entire domain and magnified view of the nose region) modelled as a wedge
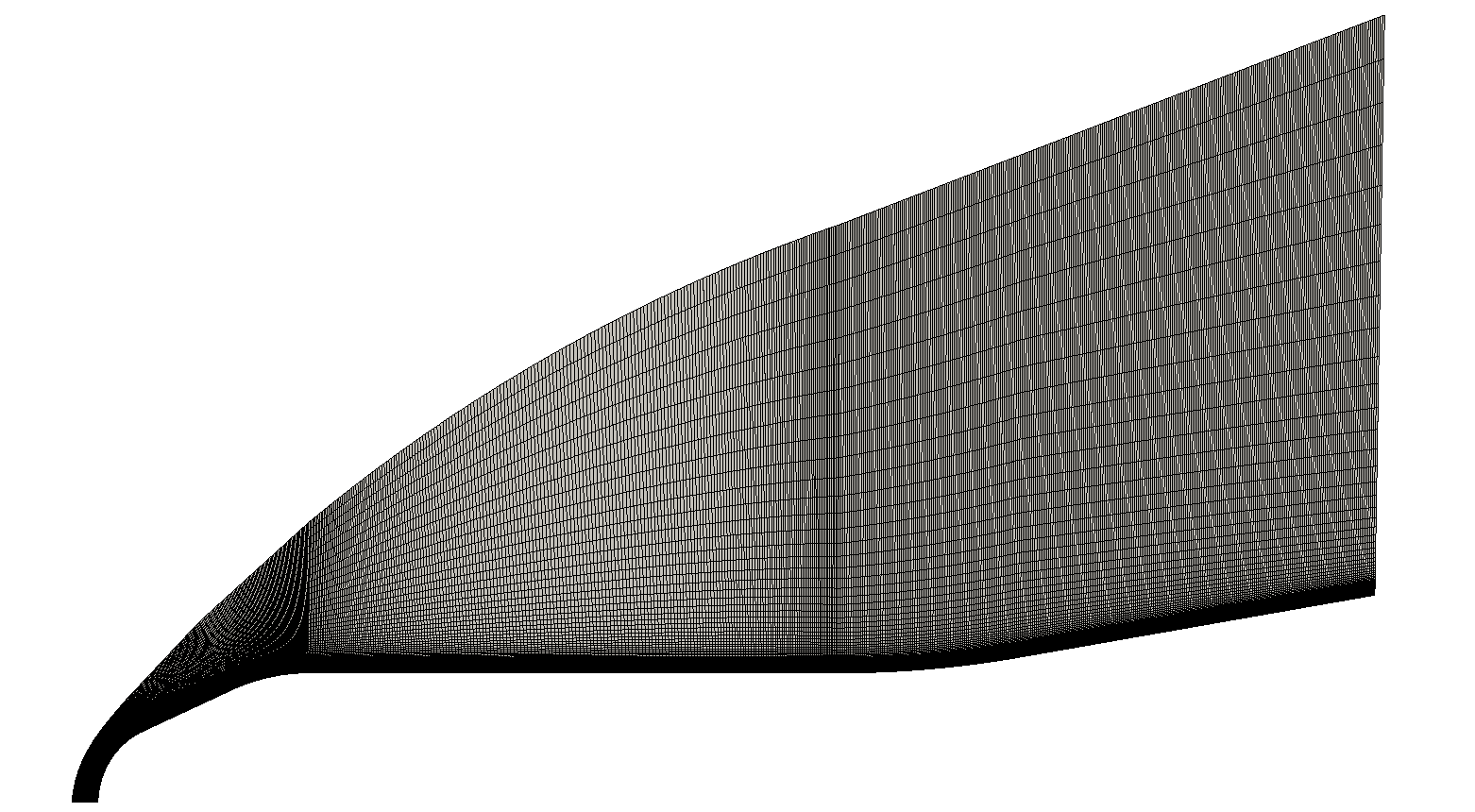
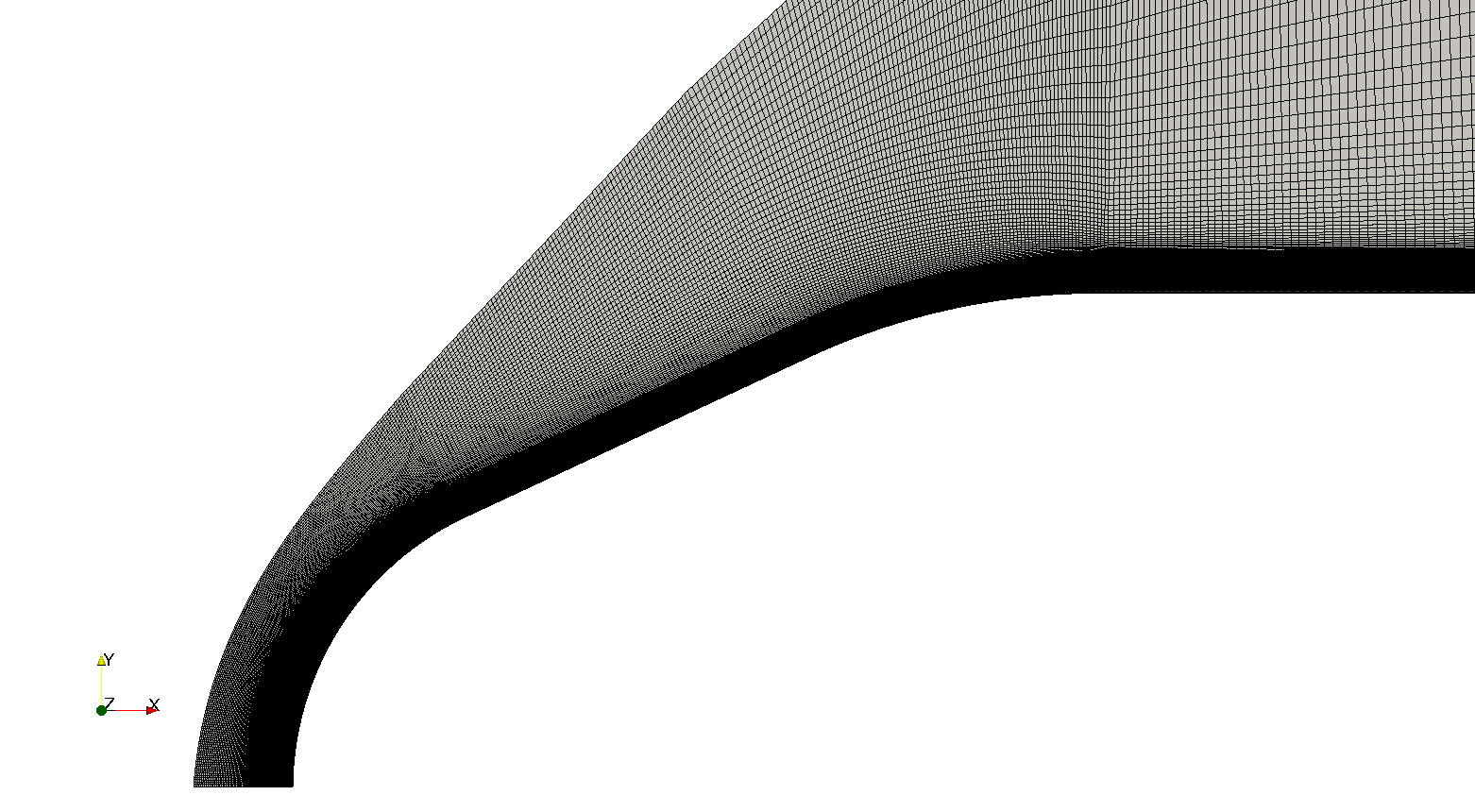
The structured mesh is aligned with the bow shock in the nose region, has 141,100 cells, and the first layer height is equal to 1 x 10-5 m.
1.2 Case conditions
The HB2 no-slip isothermal wall is maintained at a temperature of 300 K.
The fluid is Air and modelled as a single inert species.
The freestream conditions are given in
- Ma∞ = 9.59
- Re∞ = 2.1 x 106 m-1
- p∞ = 75 Pa
- T∞ = 52 K
- U∞ = (1386.2 0 0) m/s
1.3 Thermo-chemical and transport models
This test case is using the following thermo-chemical and transport models:
- calorically perfect gas
- species viscosity: Sutherland
- species thermal conductivity: Eucken<
- laminar flow
1.4 Time controls
The initial time-step is set to 1 x 10-7 s and the maximum CFL number is 0.5. The simulation end time is equal to 0.0155 s.
2. RUNNING
The following commands will copy the mesh from
./Allclean
./Allrun
To run hyFoam in parallel (say on 8 CPUs), please first edit the
./Allclean
./Allrun 8
3. MONITORING
gnuplot gnuplot/monitorResiduals
4. FLOW VISUALISATIONS IN PARAVIEW
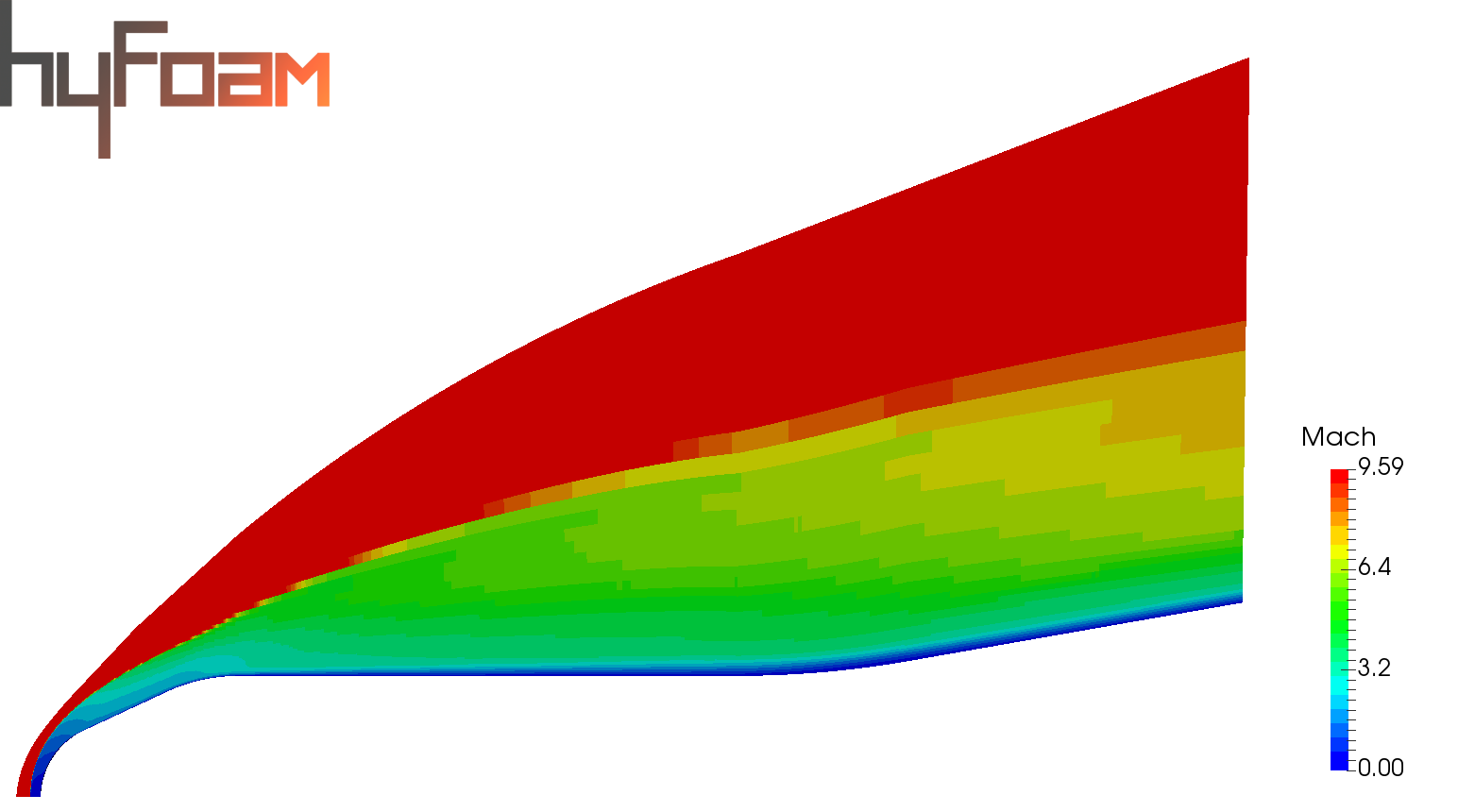
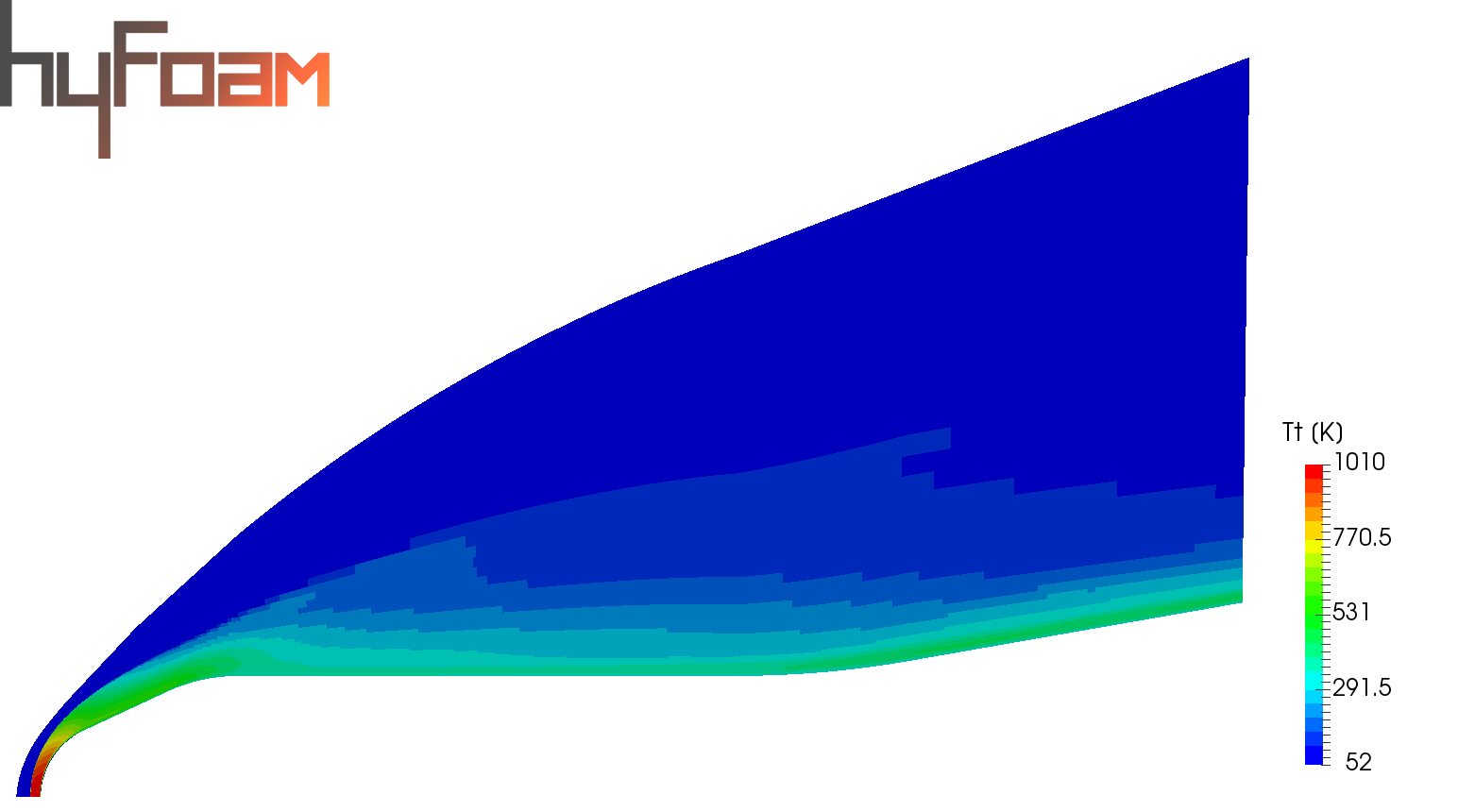
5. POST-PROCESSING
gnuplot gnuplot/monitorCd
gnuplot gnuplot/monitorIntegratedWallHeatFlux
6. SOLUTION
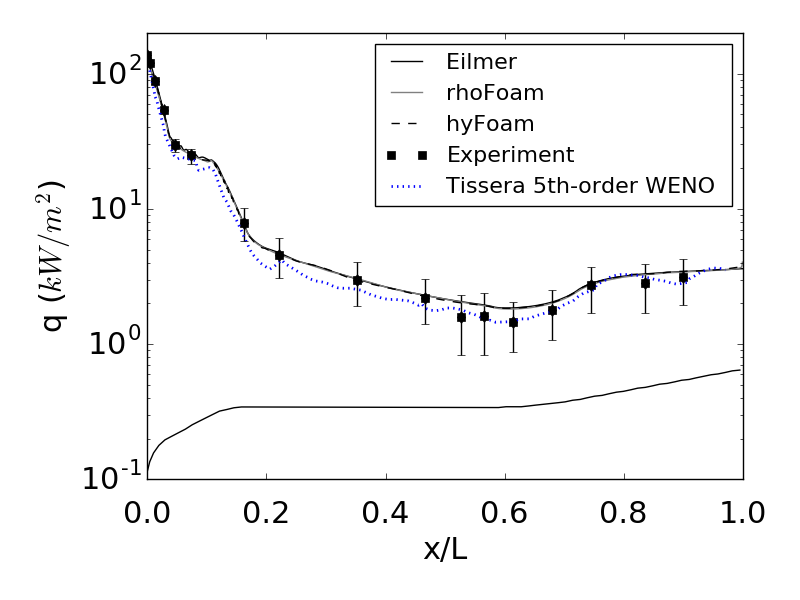
Wall heat flux along the HB2 surface (L is the body length that is equal to 0.49 m)
Contributors: Dr Jimmy-John O.E. Hoste, Dr Daniel E.R. Espinoza, Dr Vincent Casseau